Understanding Margin in a Forex Account and How to Use It
Friday, December 5, 2025Brought to you by tastyfx
Forex trading is conducted on margin, allowing traders to control large currency positions with a relatively small capital outlay. This article explains how forex margin requirements work at tastytrade, how leverage ratios are expressed, how to calculate the margin needed for a given position size, what triggers a margin call, and how to manage forex exposure responsibly to avoid forced liquidation.
What is Margin in Forex?
Margin is a good faith deposit that a trader puts up as collateral to initiate a trade. Essentially, it is the minimum amount that a trader needs in the account to open a new position. This is usually communicated as a percentage of the notional value (trade size) of the trade. The difference between the deposit and the full value of the trade is “borrowed” from the broker.
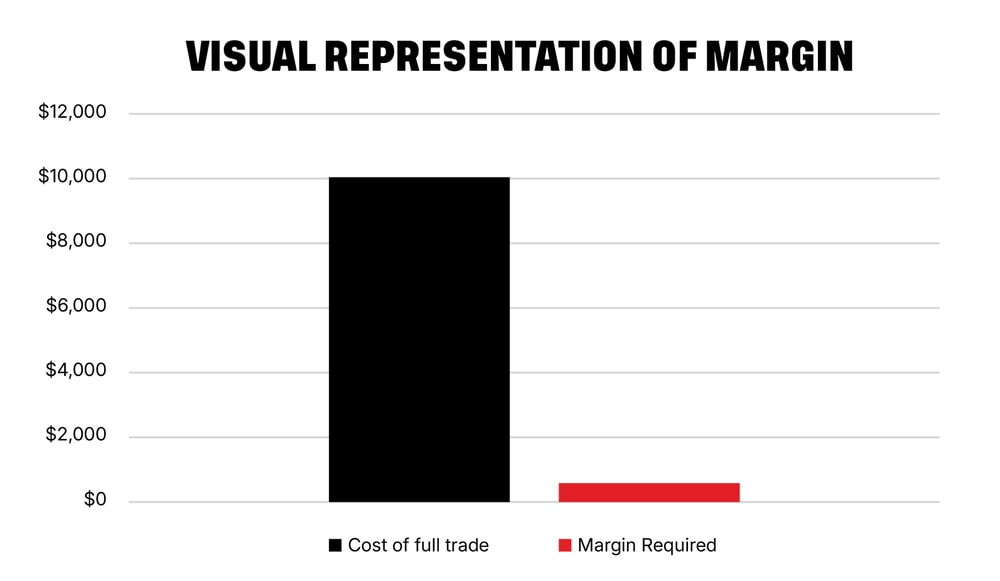
FX Margin Example
Below is a visual representation of the margin requirement relative to the full trade size, in which the trade size is $10,000 and the margin requirement is 2%.
Understanding the Connection Between Margin and Leverage
Before continuing, it is important to understand the concept of leverage. Leverage and margin are inversely correlated: the more margin required, the less leverage traders can use. This is because the trader will have to fund more of the trade with his own money and can borrow less from the broker.
Leverage has the potential to produce large profits and large losses which is why it is crucial that traders use leverage responsibly. It's important to note that leverage can vary between brokers and will differ across different jurisdictions, in line with regulatory requirements. Typical margin requirements and the corresponding leverage are shown below:
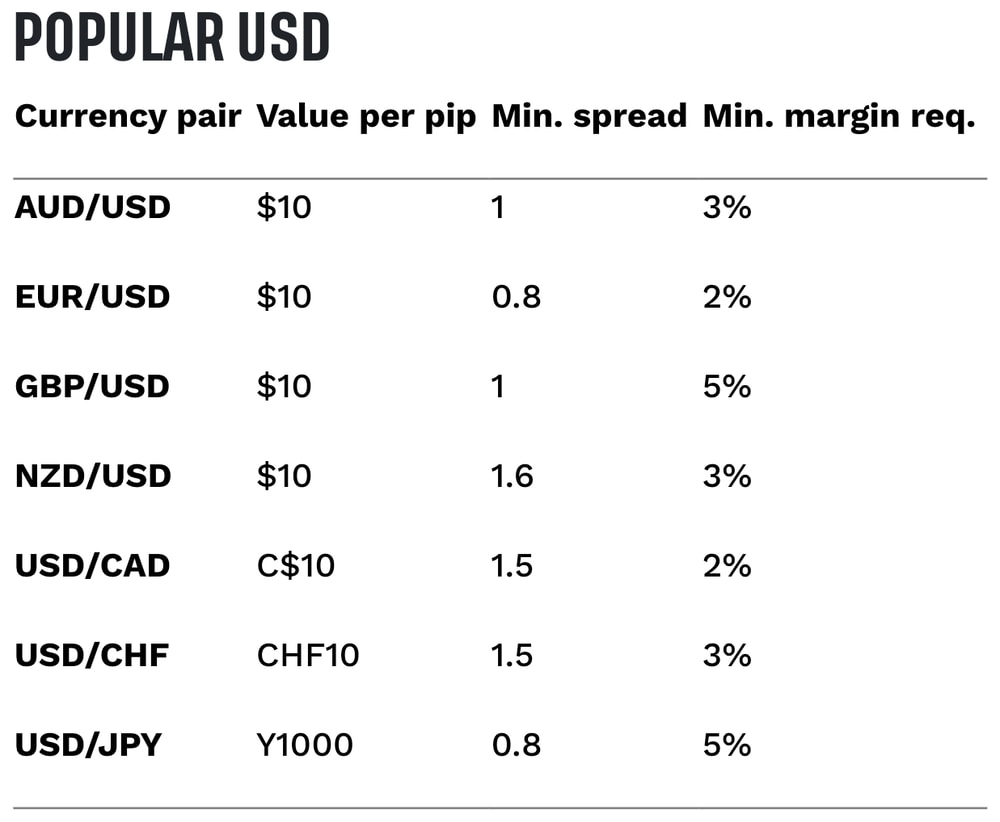
Explore tastyfx's margin requirements for all currency pairs offered on their site.
Understanding Forex Margin Requirements
Margin requirements are set out by brokers and are based on the level others are willing to assume (default risk), whilst adhering to regulatory restrictions.
Often, margin is seen as a fee a trader must pay. To clarify, this is not a transaction cost, but rather a portion of the account equity that is set aside and allocated as a margin deposit.
When trading with margin, it is important to remember that the amount of margin needed to hold open a position will ultimately be determined by the trade size. As trade size increases, traders will move to the next tier where the margin requirement (in monetary terms) will increase as well.
Margin requirements can be temporarily increased during periods of high volatility or in the lead up to events that are likely to contribute to greater-than-usual volatility.
tastyfx’s minimum margin requirements range from 2% to 25% based on what currency pair you trade.
Forex margin level = (equity / margin used) x 100
Suppose a trader has deposited $10,000 in their tastyfx account and wants to trade EUR/USD, which has a 2% minimum margin requirement. If they open a position worth $400,000 (4 standard lots), they would need $8,000 in margin (2% of $400,000). The forex margin level would equal 125% (($10,000 equity / $8,000 used margin) x 100).
For a more volatile pair like USD/TRY with a 25% margin requirement, that same $8,000 margin would only allow a $32,000 position. If the margin level approaches critical thresholds set by tastyfx, they may restrict new trades and issue a margin call to protect against excessive risk.
It is essential that traders understand the margin closeout rule specified by the broker in order to avoid the liquidation of current positions. When an account is placed on margin call, the account will need to be funded immediately to avoid the liquidation of current open positions. Brokers do this in order to bring the account equity back up to an acceptable level.
Common Forex Margin Terms
The balance of the trading account after adding current profits and subtracting current losses from the cash balance.
The amount of money (deposit) required to place a leveraged trade.
This is the portion of the account equity that is set aside to keep existing trades in the account.
The equity in the account after subtracting margin used.
This happens when your account equity drops below the acceptable level prescribed by the broker, which triggers the immediate liquidation of open positions in order to bring equity back up to the acceptable level.
This provides a measure of how well the trading account is funded, by dividing equity by the used margin and multiplying the answer by 100.
Leverage in forex is a useful financial tool that allows traders to increase their market exposure beyond the initial investment by funding a small amount of the trade and borrowing the rest from the broker. Traders should know that leverage can result in large profits and large losses.
Managing the Risks of Margin Trading
When trading on a margined account it is crucial for traders to understand how to calculate the amount of margin required per position if this is not provided on the deal ticket automatically. Be aware of the relationship between margin and leverage and how an increase in the margin required lessens the amount of leverage available to traders.
Monitor important news releases with the use of an economic calendar, should you wish to avoid trading during such volatile periods.
It is considered prudent to have a large amount of your account equity as free margin. This assists traders when avoiding margin calls and ensures that the account is sufficiently funded to get into high probability trades as soon as they appear.
Helpful Resources to Take Your Forex Trading Further
- If you are new to forex trading, stay up to date with the basics using our How to Trade Forex: Beginner’s Guide.
- It is vital to avoid mistakes with leverage. To understand how to avoid other issues traders might face, check out What is Leverage in Forex Trading & How Does It Work?
- It is highly recommended to make use of stops when trading with leverage. Learn how to use stop orders here.
- Be sure to familiarize yourself with how margin calls and violations work. Learn more here.
This article is provided by tastyfx LLC, a separate but affiliated entity and business of tastytrade Inc. Forex trading involves risk, losses may exceed deposits.
This content, including the use of actual symbols, any visual display or other reference to product, type of investment, strategy, or service offered, is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not, nor is intended to be, trading or investment advice or a recommendation that any investment product or strategy is suitable for any person.
Leveraged trading in foreign currency or off-exchange products on margin carries significant risk and may not be suitable for all investors. Losses can exceed deposits. We advise you to carefully consider whether trading is appropriate for you based upon your personal circumstances as you may lose more than you invest. The information presented does not take into account your particular investment objectives, financial situation and/or needs and is not a substitute for obtaining professional advice from a qualified person, firm, or corporation, where required. You are advised to perform an independent investigation of any transaction you intend to execute in order to ensure that transaction is suitable for you. Information presented by tastyfx should not be construed nor interpreted as financial advice.