Short Call Vertical Spread Options Strategy Explained
Short Call Vertical Spread Summary
- A short call vertical spread is a bearish position involving a short and long call with different strike prices in the same expiration.
- When setting up a short call spread, the short call is more expensive than the long call since the short call is closer to the money, resulting in net credit.
- Buying a call at a higher strike price against the short call provides upside protection and reduces the maximum profit potential due to the cost of the long call.
- The credit received for the short call vertical spread is an investor's max profit if it expires OTM and is worthless at expiration.
- The max loss of a short vertical call spread is known upfront by subtracting the credit received from the spread width. However, losses can be more due to short stock assignment if the underlying closes and expires between the spread.
Short Call Vertical Spread
A short call credit spread is a defined-risk bearish strategy, where the trader wants the underlying price to fall. A short call vertical spread consists of two call option contracts in the same expiration: a short call closer to the stock price and a long call further out-of-the-money (OTM). The short call acts as a hedge in the same expiration. The short call is always more valuable than the long call in a short call vertical spread, resulting in a net credit the investor receives upfront after selling it. The goal is for the short call spread to lose value.
A defined risk spread is a strategy that caps your maximum loss potential. Max loss occurs when the underlying rises and breaches both legs of the call credit spread, causing both legs to go in-the-money (ITM) and trade at its full value, which is its spread width. When preparing a short call vertical spread order, you know what is at risk at order entry.
One characteristic of a short call vertical is that the overall credit received is lower than just selling a naked call, because it requires purchasing a call to define the risk. In other words, you must pay for protection.
However, one potential benefit of a defined-risk spread is that it requires a lower buying power requirement since we know the max loss ahead of time, which can be more capital efficient for accounts with limited buying power.
Like any other short options strategy, you will initially receive a credit when selling a call vertical spread. The value of the call spread will decrease when the underlying falls in price, which is exactly what you want for your short call vertical spread to be profitable to keep the credit.
Additionally, the value of a short call vertical spread can decrease over time when the price of the underlying remains constant, and the spread remains OTM due to time decay. The ideal scenario for a short call vertical spread is that it remains OTM at expiration, expires worthless, and yields a max profit which is the credit received on trade entry, less commissions and fees. The trade can also be “bought back” (covered) for less than the credit received upfront to yield a profit or bought back for more than the credit received upfront to realize a loss. In other words, the trade does not need to be held to expiration.
On the other hand, the max loss scenario for a short call vertical spread is that it moves in-the-money (ITM). This happens if the stock price rises and trades above the long call strike. The spread can trade for a maximum value of the distance between the strikes, and the trader would have to buy back the spread to close the trade. At expiration, max loss would be realized in this case, or the trader can buy back the spread for potentially less than max loss before expiration if they choose to exit the position.
When a credit spread expires fully ITM, the short and long call contracts convert to 100 short and long shares of stock respectively, and the trader is left with no position and realizes max loss.
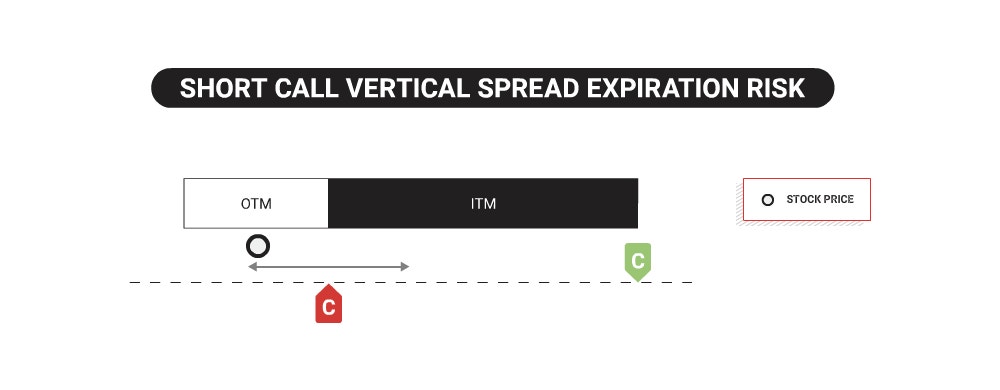
Expiration Risk for Short Call Vertical Spreads
A defined-risk vertical spread is no longer a defined risk position if one leg of the spread expires in the money, and the other does not. The risk lies with pin risk on the day of expiration, which is the risk surrounding the uncertainty of where the underlying will close to determine whether an option is in or out of the money. Options that expire in the money by $0.01 or more are auto-exercised, resulting in the short call option converting to 100 short shares of stock. In the case of a short call vertical spread, a partially ITM spread will convert to 100 short shares at the short strike price, and the OTM long call option would not get auto-exercised to offset the short shares [with long shares]. When you end up with short shares, the risk is unlimited to the upside, so manage accordingly.
Additionally, any options strategy involving short options, including a short call vertical, may face after-hours risk on the day of expiration. In summary, although the vertical may have expired OTM based on the stock's closing print, an OTM short call option can become ITM based on any extreme upward price movement after the market close, resulting in an unexpected assignment of short shares. As a result, the investor would assume the (unlimited) risk of 100 short shares per contract assigned. The only way to eliminate after-hours risk is by closing any short options positions before expiration.
Due to the risk of getting assigned short shares, it's crucial to have a plan, like closing or rolling the position before expiration, to avoid this particular assignment risk, especially when the account does not have sufficient account equity to take on the resulting position. Please visit the tastytrade Help Center to learn more about Expiration Risk.
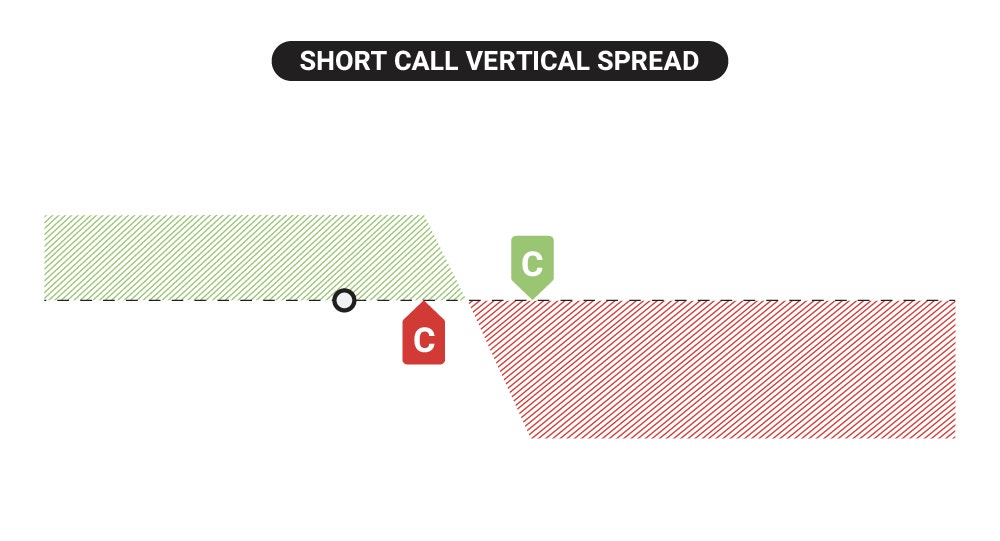
Profit & Loss Diagram of a Short Call Vertical Spread
A short call vertical spread is a bearish trade that can yield a profit if the underlying remains below the short call strike until expiration, illustrated with a red C flag on the P/L diagram. As the share price drops or remains constant below the short call strike price, the value of the call credit spread can decrease over time depending on various factors such as changes in volatility or how fast the stock price falls.
The initial credit received after selling a call vertical spread is an investor's max profit if it expires OTM and is worthless, as indicated where the green profit zone flattens above the x-axis. Losses on the call credit spread occur when the underlying rises above the breakeven price, as illustrated where the green and red zones converge on the x-axis.
As mentioned, defined-risk spreads are subject to expiration risk and are no longer defined risk if the underlying closes between the vertical spread.
Lastly, investors can experience their max loss potential on a short call vertical spread if it expires ITM entirely. However, the long call helps cap losses, as the green C flag indicates. As a result, the maximum loss on a short call vertical is the initial credit received minus the spread width, which the flattened red zone of the diagram illustrates.
What’s Required for a Short Call Vertical Spread?
Two call options in the same expiration.
- Sell to Open -1 short call
- Buy to Open +1 long call (any strike price above the short call)
Example of a Short Call Vertical Spread
XYZ currently trading @ $50
- -1 XYZ 55-strike call @ $3 credit
- +1 XYZ 60-strike call @ $1.50 debit
Collect a $1.50 credit ($150 total)
Spread Width: Long strike – Short strike = 60 – 55 = $5
Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
Time Decay Affect | Works in your favor by decaying the value of the spread |
Max Profit | Total credit received |
Max Loss | Total credit received – (Spread width x 100) $150 - ($5 x 100) = -$3.5 (-$350) |
Breakeven Price (at expiration) | Short strike price + Credit received $55 + $1.50 = $56.50 |
Buying Power Requirement | -$350 (max loss calculation) |
Account Type Required | Margin and IRA |
Other Names | Bear call spread Credit call spread Short call spread Short call vertical |
Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
Time Decay Affect | Works in your favor by decaying the value of the spread |
Max Profit | Total credit received |
Max Loss | Total credit received – (Spread width x 100) $150 - ($5 x 100) = -$3.5 (-$350) |
Breakeven Price (at expiration) | Short strike price + Credit received $55 + $1.50 = $56.50 |
Buying Power Requirement | -$350 (max loss calculation) |
Account Type Required | Margin and IRA |
Other Names | Bear call spread Credit call spread Short call spread Short call vertical |
How to Place a Short Call Vertical Spread Order
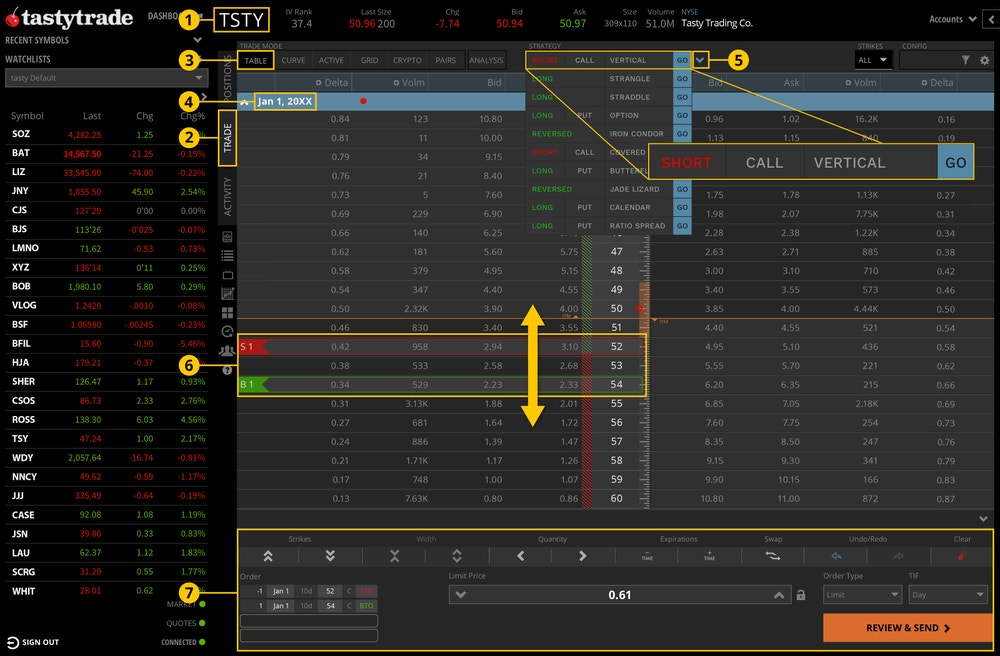
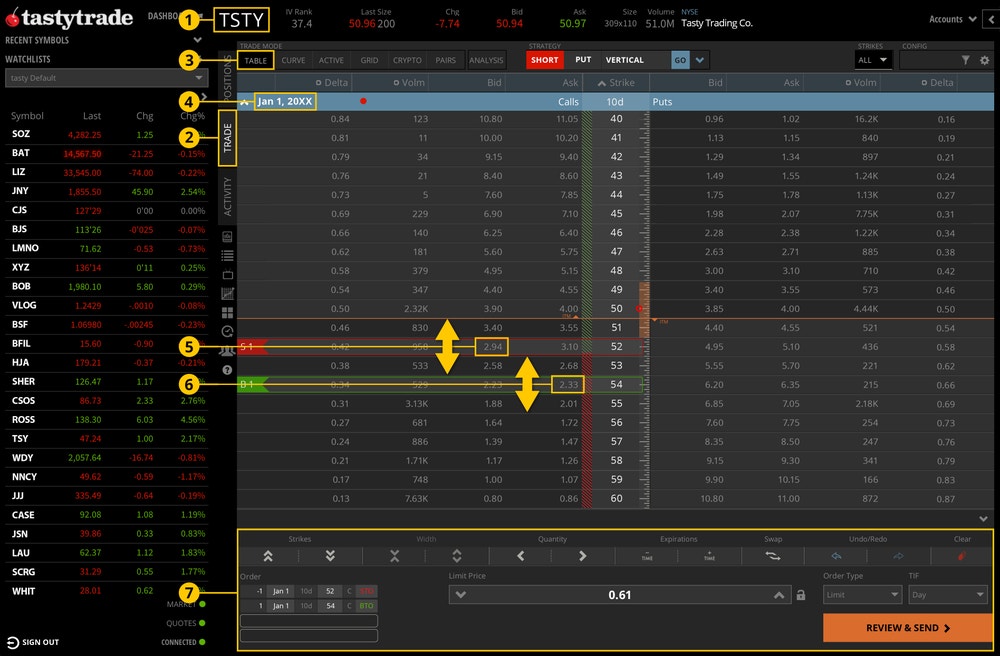
Using the Strategy Menu
- Enter a symbol.
- Navigate to the Trade tab.
- Go to the Table mode.
- Click on an expiration date to expand.
- Click the Strategy Menu and locate the Vertical strategy. From left to right, click each column to display Short, Call, and Go.
- The long strike order will display a green bar, and the short strike will display in a red bar in the expanded expiration. Drag each strike up or down to the desired strike.
- Go to the order ticket to determine the quantity, price, time-in-force (TIF), etc. before clicking "Review & Send." Review everything including commissions and fees before sending the order.
Building it Manually
- Enter a symbol.
- Navigate to the Trade tab.
- Go to the Table mode.
- Click on an expiration date to expand.
- Click the Bid price of the short leg.
- Click the Ask price of the long leg.
- Go to the order ticket to determine the quantity, price, time-in-force (TIF), etc. before clicking "Review & Send." Review everything including commissions and fees before sending the order.
Options involve risk and are not suitable for all investors as the special risks inherent to options trading may expose investors to potentially significant losses. Please read Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options before deciding to invest in options.
All investments involve risk of loss. Please carefully consider the risks associated with your investments and if such trading is suitable for you before deciding to trade certain products or strategies. You are solely responsible for making your investment and trading decisions and for evaluating the risks associated with your investments.
Multi-leg option strategies incur higher transaction costs as they involve multiple commission charges.